What: Developed a real-time, voice-based emotion detector capable of distinguishing between
anger and sadness.
Why:
To explore how audio signal parameters can be used to classify emotional states and to gain experience
with signal processing and Python-Arduino communication.
How: My team and I selected four acoustic parameters to differentiate emotions:
zero-crossing rate, short-term energy, harmonic-to-noise ratio, and mean pitch. We built the prototype on a
breadboard, using a microphone and two LEDs -- one each for anger and sadness detection.
Using Arduino IDE, I programmed the Arduino to collect microphone data over 3-second intervals. These ADC values
were sent over serial to Python, which converted the signal into a .wav file and extracted the chosen
parameters. The values were compared to threshold ranges derived from testing labeled angry and sad voice
samples. If at least 3 of the 4 thresholds were met for anger, Python sent a signal back to Arduino to light the
corresponding LED.
Results
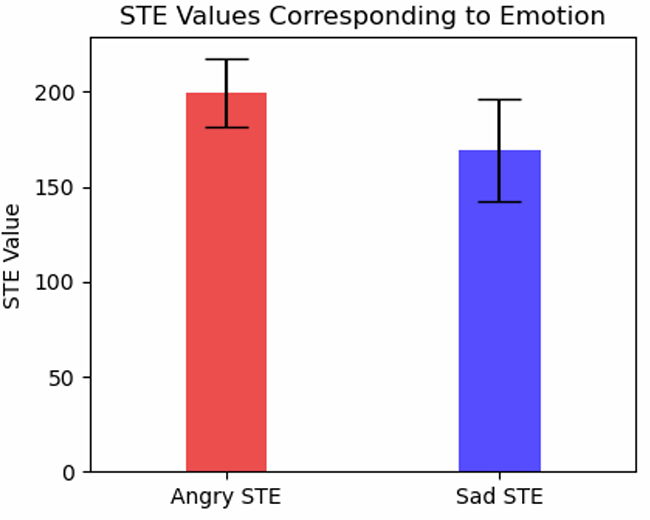
The system achieved 80% classification accuracy over 10 test trials (5 angry and 5 sad samples), which
we deemed as successful!


